ICCV 2023 - Selection of papers
Note
The purpose of this post is to compile a number of papers that have been presented at the 2023 International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) and which we feel may be of interest for people working in deep learning and/or medical imaging.
You can check all papers on CVF open access for ICCV 2023 main conference and workshops.
Summary
- Diffusion Models as Masked Autoencoders
- Audiovisual Masked Autoencoders
- BlindHarmony: “Blind” Harmonization for MR Images via Flow Model
- Preserving Modality Structure Improves Multi-Modal Learning
- Texture Learning Domain Randomization for Domain Generalized Segmentation
- LIMITR: Leveraging Local Information for Medical Image-Text Representation
- MedKLIP: Medical Knowledge Enhanced Language-Image Pre-Training for X-ray Diagnosis
- Stochastic Segmentation with Conditional Categorical Diffusion Models
- Scale-MAE: A Scale-Aware Masked Autoencoder for Multiscale Geospatial Representation Learning
- ImbSAM: A Closer Look at Sharpness-Aware Minimization in Class-Imbalanced Recognition
- Other papers
Diffusion Models as Masked Autoencoders
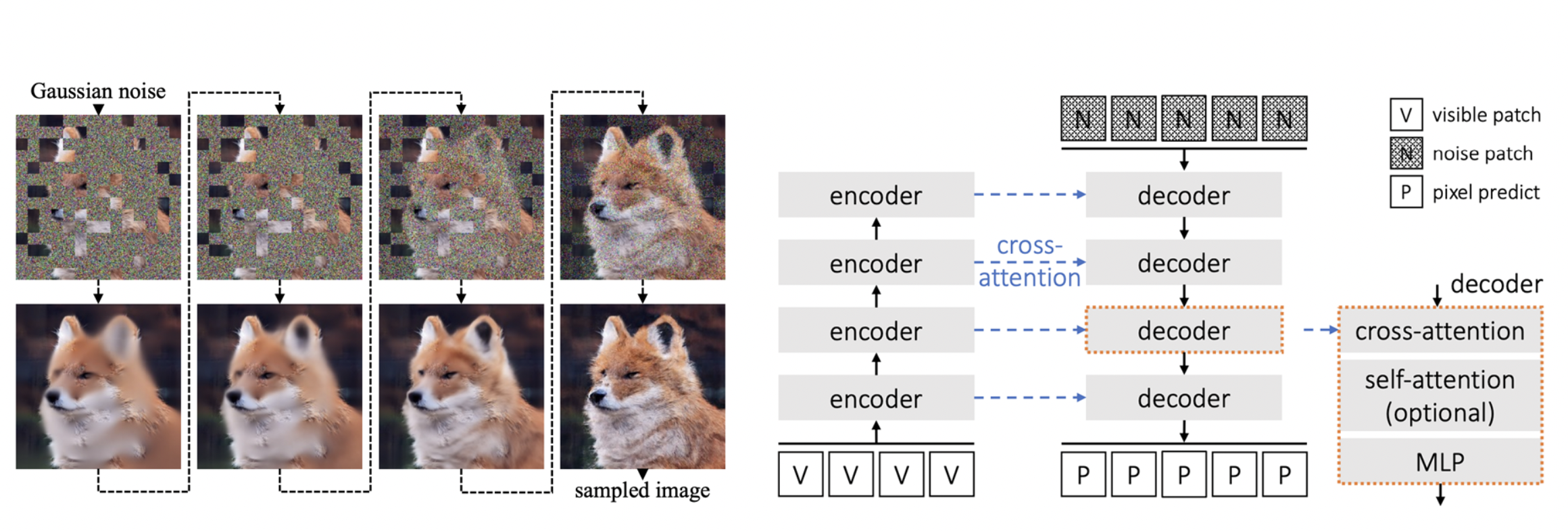
C. Wei, K. Mangalam, P.-Y. Huang, Y. Li, H. Fan, H. Xu, H. Wang, C. Xie, A. Yuille, C. Feichtenhofer, Diffusion Models as Masked Autoencoders, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“While directly pre-training with diffusion models does not produce strong representations, we condition diffusion models on masked input and formulate diffusion models as masked autoencoders (DiffMAE). Our approach is capable of (i) serving as a strong initialization for downstream recognition tasks, (ii) conducting high-quality image inpainting, and (iii) being effortlessly extended to video where it produces state-of-the-art classification accuracy.”
Audiovisual Masked Autoencoders
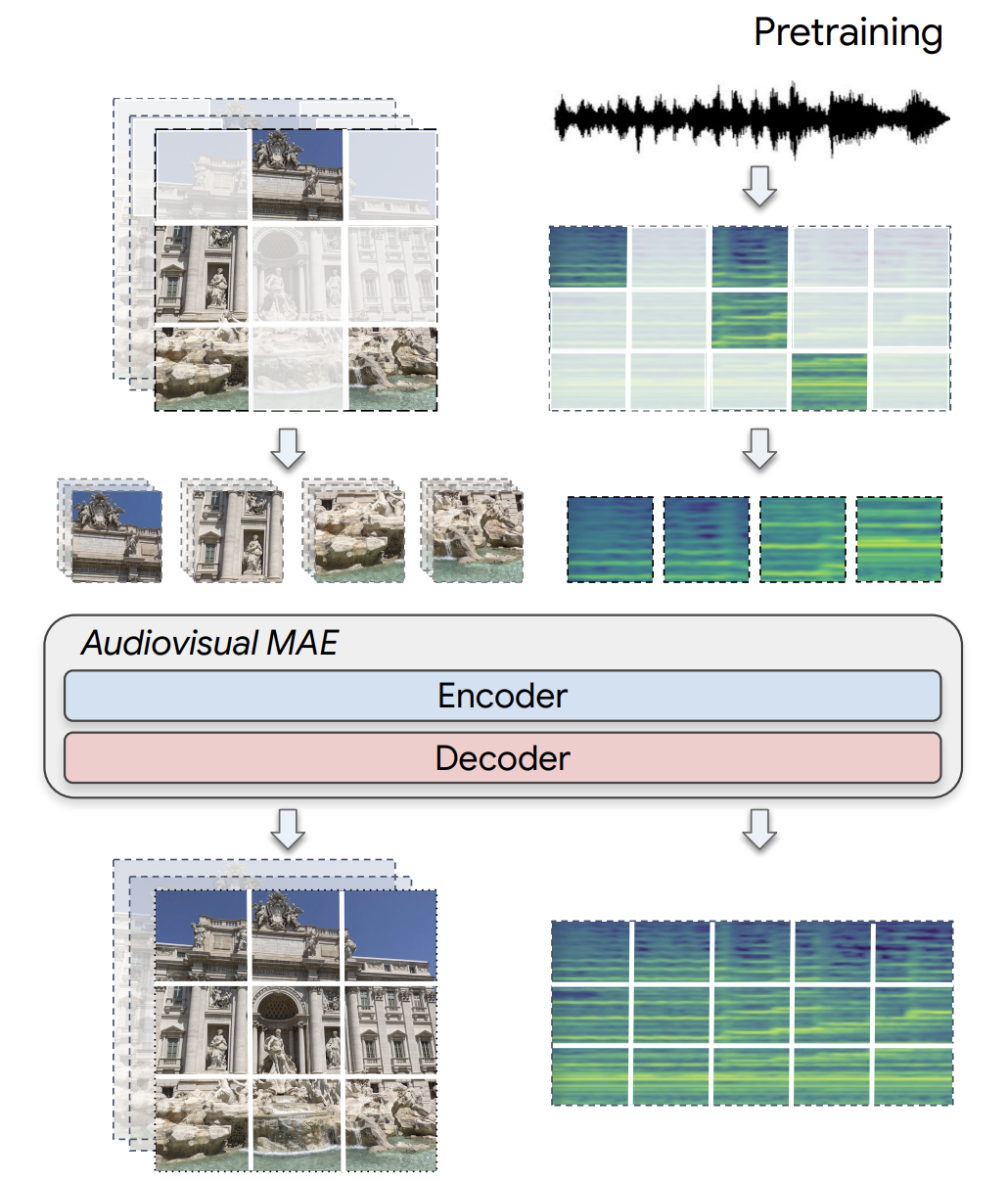
M.-I. Georgescu, E. Fonseca, R. Tudor Ionescu, M. Lucic, C. Schmid, A. Arnab, Audiovisual Masked Autoencoders, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“we study various pretraining architectures and objectives within the masked autoencoding framework, motivated by the success of similar methods in natural language and image understanding. We show that we can achieve significant improvements on audiovisual downstream classification tasks, surpassing the state-of-the-art on VGGSound and AudioSet.”
BlindHarmony: “Blind” Harmonization for MR Images via Flow Model
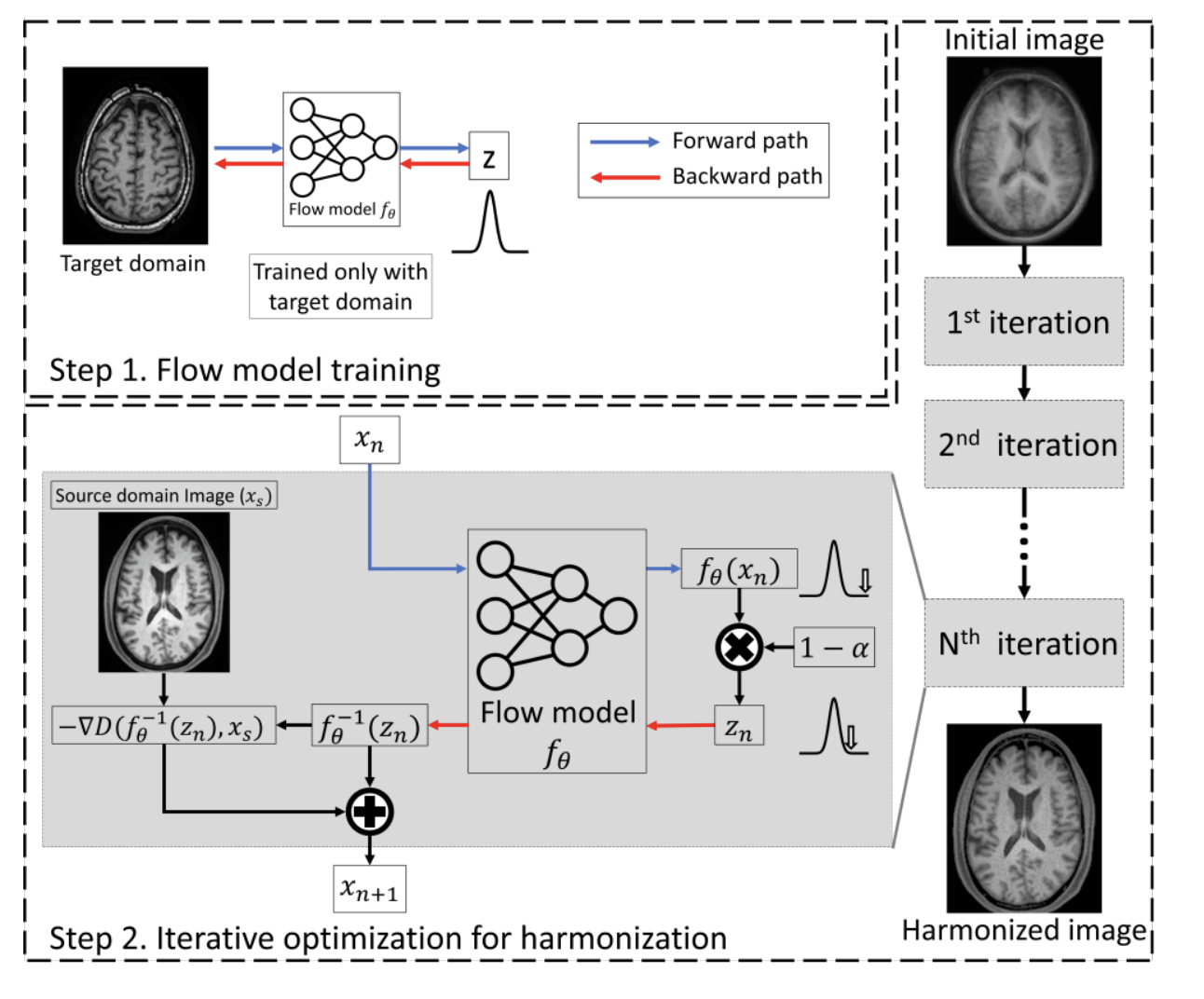
H. Jeong, H. Byun, D. Un Kang, J. Lee, BlindHarmony: “Blind” Harmonization for MR Images via Flow Model, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“we propose a novel concept called ‘Blind Harmonization’, which utilizes only target domain data for training but still has the capability to harmonize images from unseen domains. For the implementation of blind harmonization, we developed BlindHarmony using an unconditional flow model trained on target domain data. The harmonized image is optimized to have a correlation with the input source domain image while ensuring that the latent vector of the flow model is close to the center of the Gaussian distribution.”
Preserving Modality Structure Improves Multi-Modal Learning
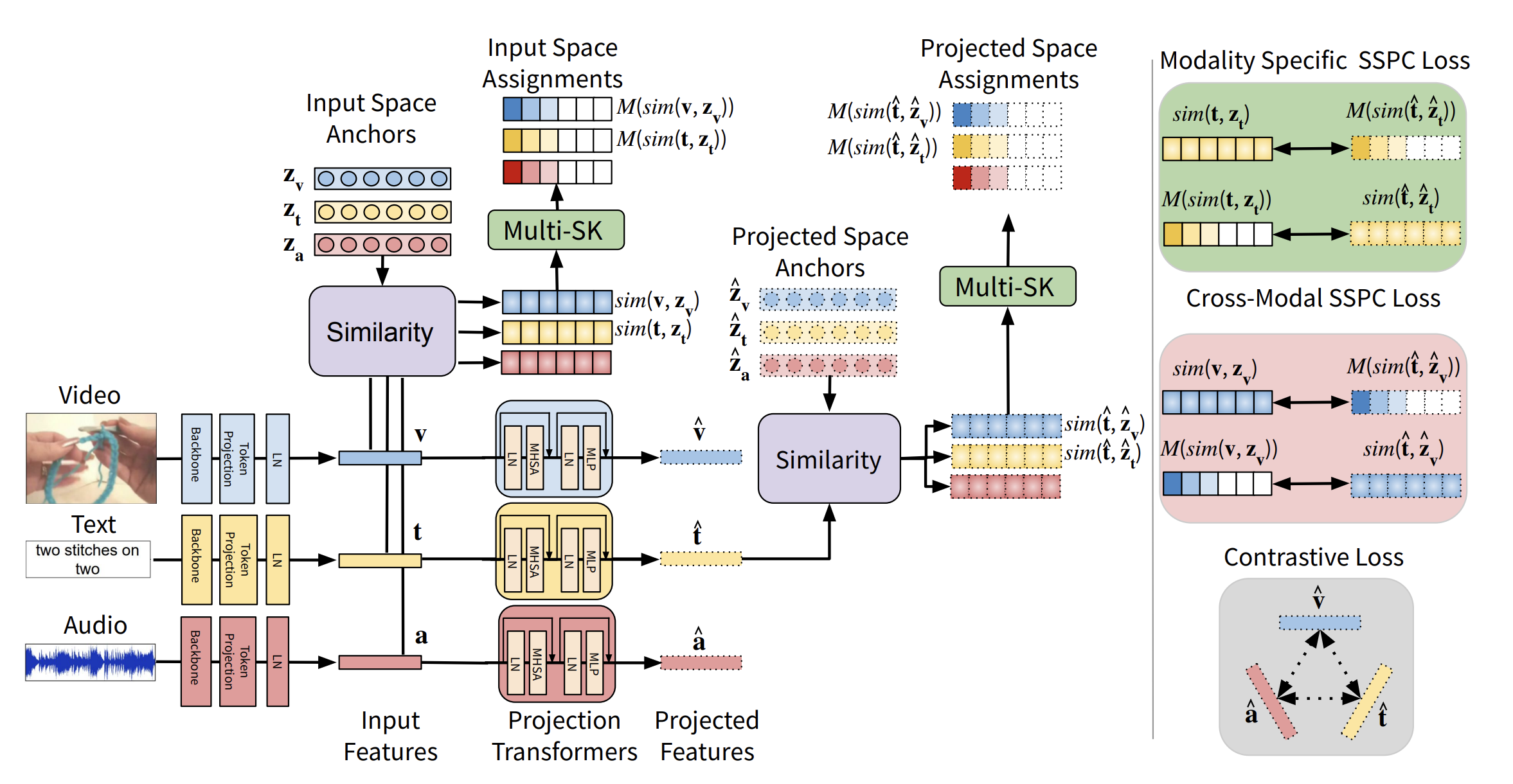
S. Swetha, M. Nayeem Rizve, N. Shvetsova, H. Kuehne, M. Shah, Preserving Modality Structure Improves Multi-Modal Learning, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“In this context, we propose a novel Semantic-Structure-Preserving Consistency approach to improve generalizability by preserving the modality-specific relationships in the joint embedding space. To capture modality-specific semantic relationships between samples, we propose to learn multiple anchors and represent the multifaceted relationship between samples with respect to their relationship with these anchors. To assign multiple anchors to each sample, we propose a novel Multi-Assignment Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm.”
Texture Learning Domain Randomization for Domain Generalized Segmentation
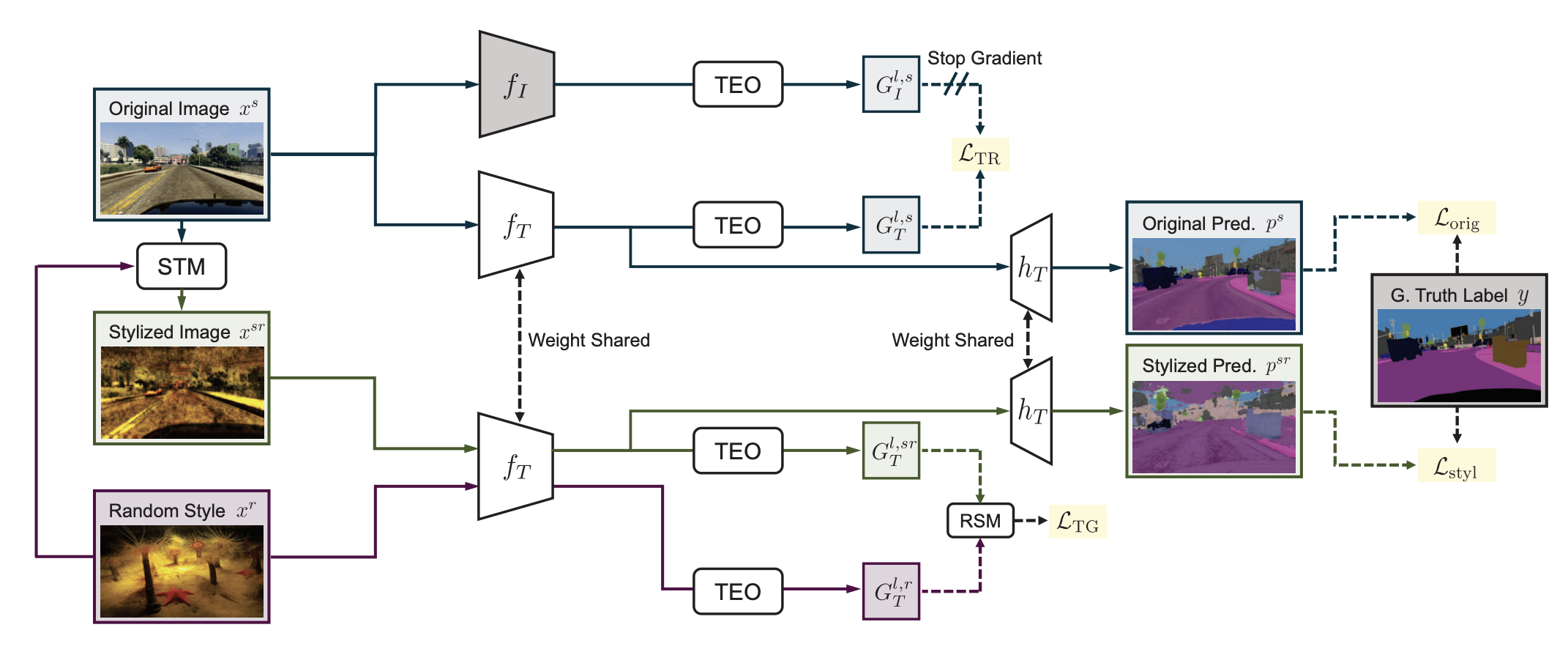
S. Kim, D.-H. Kim, H. Kim, Texture Learning Domain Randomization for Domain Generalized Segmentation, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“This paper argues that leveraging texture is crucial for improving performance in DGSS. Specifically, we propose a novel framework, coined Texture Learning Domain Randomization (TLDR). TLDR includes two novel losses to effectively enhance texture learning in DGSS: (1) a texture regularization loss to prevent overfitting to source domain textures by using texture features from an ImageNet pretrained model and (2) a texture generalization loss that utilizes random style images to learn diverse texture representations in a self-supervised manner”
LIMITR: Leveraging Local Information for Medical Image-Text Representation
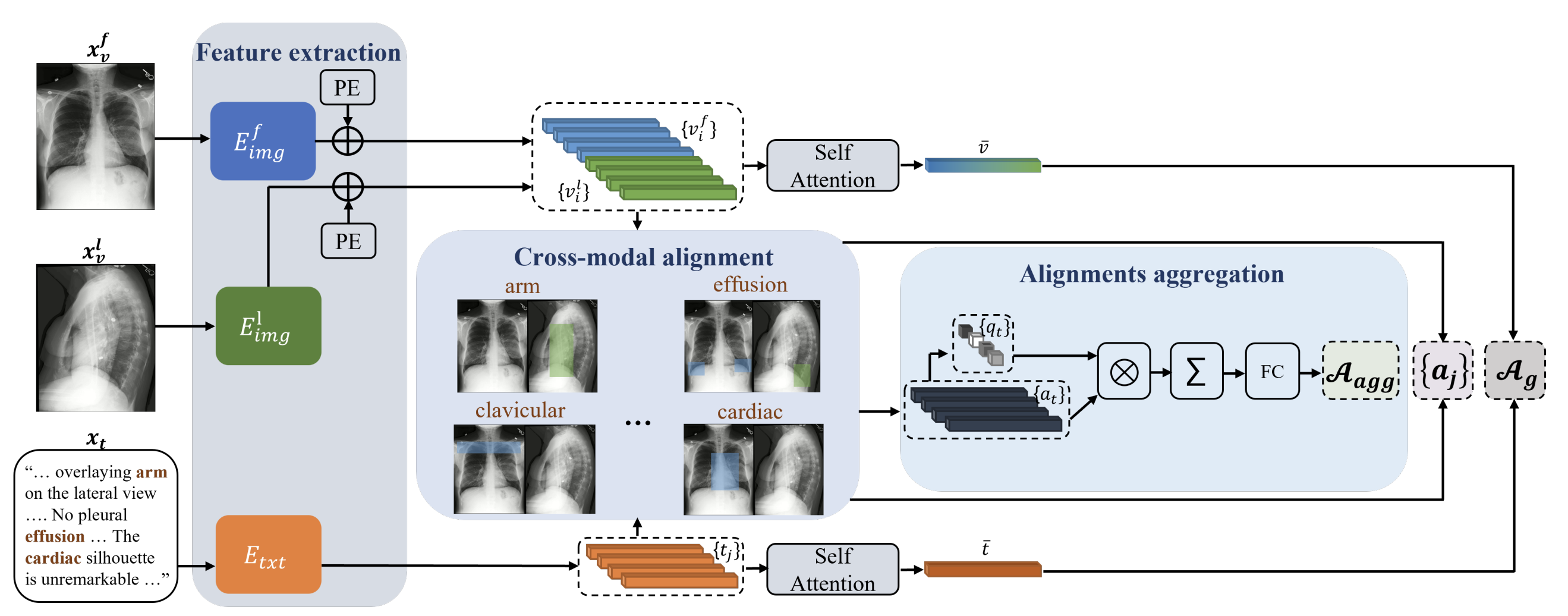
G. Dawidowicz, E. Hirsch, A. Tal, LIMITR: Leveraging Local Information for Medical Image-Text Representation, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
” It presents a new model that learns a joint X-ray image & report representation. The model is based on a novel alignment scheme between the visual data and the text, which takes into account both local and global information. Furthermore, the model integrates domain-specific information of two types—lateral images and the consistent visual structure of chest images.”
MedKLIP: Medical Knowledge Enhanced Language-Image Pre-Training for X-ray Diagnosis
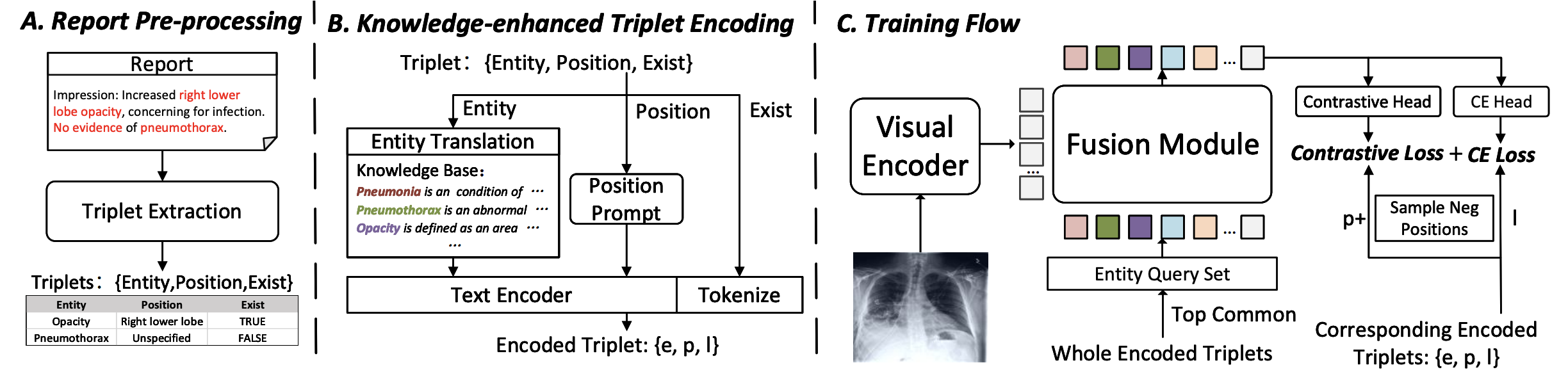
C. Wu, X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, W. Xie, MedKLIP: Medical Knowledge Enhanced Language-Image Pre-Training for X-ray Diagnosis, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“First, unlike existing works that directly process the raw reports, we adopt a novel triplet extraction module to extract the medical-related information, avoiding unnecessary complexity from language grammar and enhancing the supervision signals; Second, we propose a novel triplet encoding module with entity translation by querying a knowledge base, to exploit the rich domain knowledge in medical field, and implicitly build relationships between medical entities in the language embedding space; Third, we propose to use a Transformer-based fusion model for spatially aligning the entity description with visual signals at the image patch level, enabling the ability for medical diagnosis;”
Stochastic Segmentation with Conditional Categorical Diffusion Models
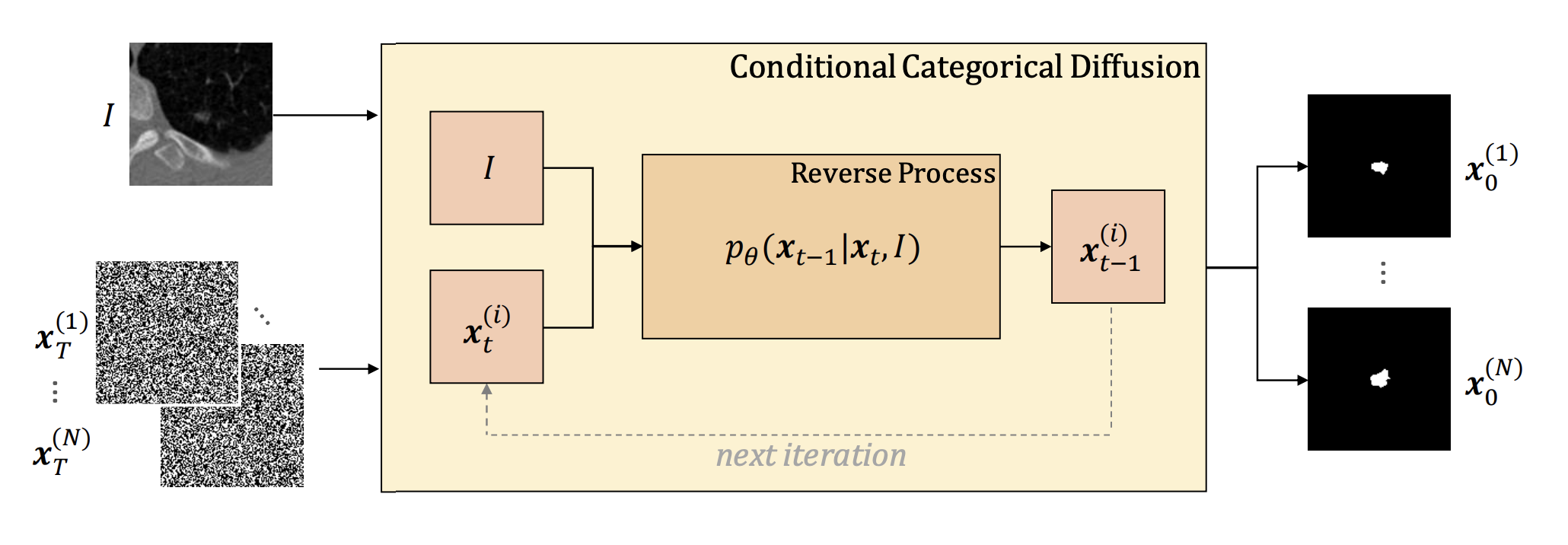
L. Zbinden, L. Doorenbos, T. Pissas, A. T. Huber, R. Sznitman, P. Márquez-Neila, Stochastic Segmentation with Conditional Categorical Diffusion Models, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“we propose a conditional categorical diffusion model (CCDM) for semantic segmentation based on Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. Our model is conditioned to the input image, enabling it to generate multiple segmentation label maps that account for the aleatoric uncertainty arising from divergent ground truth annotations.”
Scale-MAE: A Scale-Aware Masked Autoencoder for Multiscale Geospatial Representation Learning
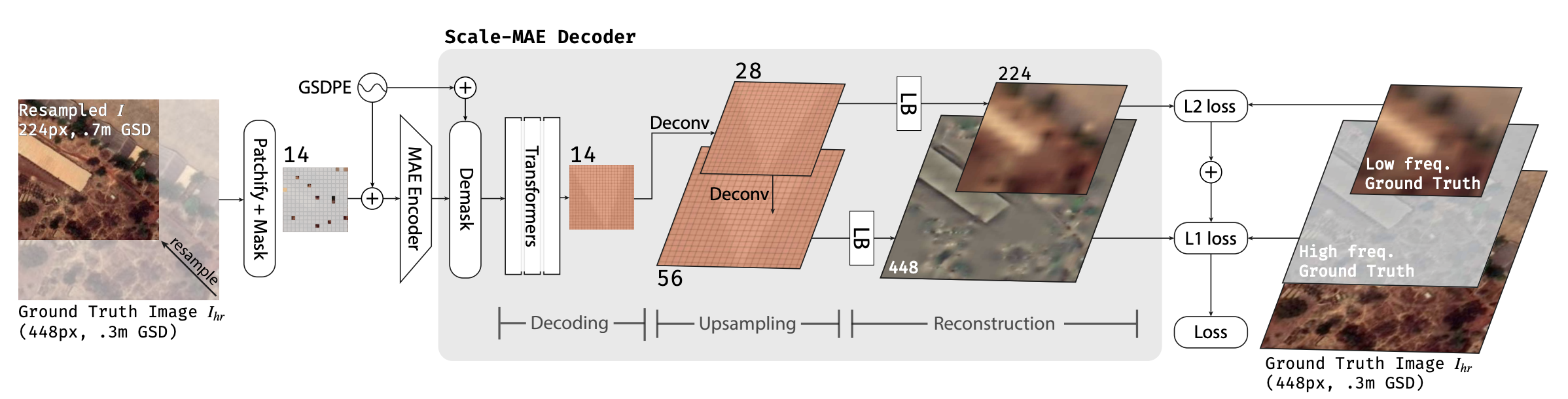
C. J. Reed, R. Gupta, S. Li, S. Brockman, C. Funk, B. Clipp, K. Keutzer, S. Candido, M. Uyttendaele, T. Darrell, Scale-MAE: A Scale-Aware Masked Autoencoder for Multiscale Geospatial Representation Learning, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“In this paper, we present Scale-MAE, a pretraining method that explicitly learns relationships between data at different, known scales throughout the pretraining process. Scale-MAE pretrains a network by masking an input image at a known input scale, where the area of the Earth covered by the image determines the scale of the ViT positional encoding, not the image resolution.”
ImbSAM: A Closer Look at Sharpness-Aware Minimization in Class-Imbalanced Recognition
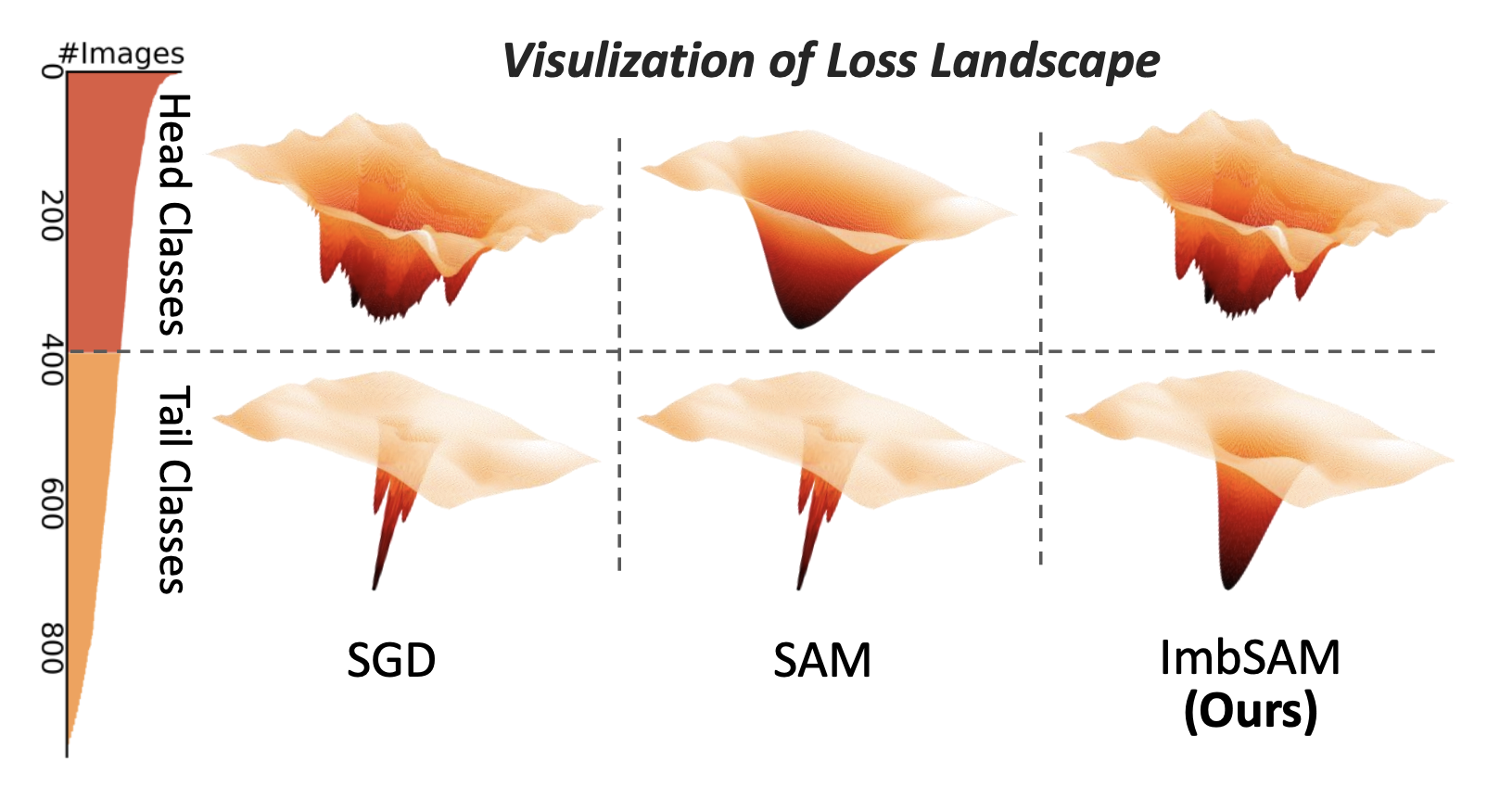
Y. Zhou, Y. Qu, X. Xu, H. Shen, ImbSAM: A Closer Look at Sharpness-Aware Minimization in Class-Imbalanced Recognition, Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023.
“Class imbalance is a common challenge in real-world recognition tasks, where the majority of lasses have few samples, also known as tail classes. We address this challenge with the perspective of generalization and empirically find that the promising Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) fails to address generalization issues under the class-imbalanced setting. […] To overcome this bottleneck, we leverage class priors to restrict the generalization scope of the class-agnostic SAM and propose a class-aware smoothness optimization algorithm named mbalanced-SAM (ImbSAM).”
Other papers
Transfer, low-shot, continual, long-tail learning
- W. Cho, J. Park, T. Kim, Complementary Domain Adaptation and Generalization for Unsupervised Continual Domain Shift Learnings, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“In this paper, we propose Complementary Domain Adaptation and Generalization (CoDAG), a simple yet effective learning framework that combines domain adaptation and generalization in a complementary manner to achieve three major goals of unsupervised continual domain shift learning: adapting to a current domain, generalizing to unseen domains, and preventing forgetting of previously seen domains. Our approach is modelagnostic, meaning that it is compatible with any existing domain adaptation and generalization algorithms.”
- D. Bhattacharjee, S. Süsstrunk, M. Salzmann, Vision Transformer Adapters for Generalizable Multitask Learning, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“We introduce the first multitasking vision transformer adapters that learn generalizable task affinities which canbe applied to novel tasks and domains. Integrated into an off-the-shelf vision transformer backbone, our adapters can simultaneously solve multiple dense vision tasks in a parameter-efficient manner, unlike existing multitasking transformers that are parametrically expensive.”
- N. K. Dinsdale, M. Jenkinson, A. IL Namburete, SFHarmony: Source Free Domain Adaptation for Distributed Neuroimaging Analysis, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we propose an Unsupervised Source-Free Domain Adaptation (SFDA) method, SFHarmony. Through modelling the imaging features as a Gaussian Mixture Model and minimising an adapted Bhattacharyya distance between the source and target features, we can create a model that performs well for the target data whilst having a shared feature representation across the data domains, without needing access to the source data for adaptation or target labels.”
- D. Peng, P. Hu, Q. Ke, J. Liu, Diffusion-based Image Translation with Label Guidance for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
” Concretely, we formulate cross-domain image translation as a denoising diffusion process and utilize a novel Semantic Gradient Guidance (SGG) method to constrain the translation process, conditioning it on the pixel-wise source labels. Additionally, a Progressive Translation Learning (PTL) strategy is devised to enable the SGG method to work reliably across domains with large gaps.”
- K. Borup, C. Perng Phoo, B. Hariharan, Distilling from Similar Tasks for Transfer Learning on a Budget, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we show how to use task similarity metrics to select a single suitable source model to distill from, and that a good selection process is imperative for good downstream performance of a target model. We dub this approach DISTILLNEAREST. […] we propose a weighted multi-source distillation method to distill multiple source models trained on different domains weighted by their relevance for the target task into a single efficient model (named DISTILLWEIGHTED).
- V. Udandarao, A. Gupta, S. Albanie, SuS-X: Training-Free Name-Only Transfer of Vision-Language Models, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we pursue a different approach and explore the regime of training-free “name-only transfer” in which the only knowledge we possess about the downstream task comprises the names of downstream target categories. We propose a novel method, SuS-X, consisting of two key building blocks— “SuS” and “TIP-X”, that requires neither intensive finetuning nor costly labelled data.”
Self-, semi-, weakly-, unsupervised learning
- Y. Duan, Z. Zhao, L. Qi, L. Zhou, L. Wang, Y. Shi, Towards Semi-supervised Learning with Non-random Missing Labelss, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“In label Missing Not At Random (MNAR), the labeled and unlabeled data fall into different class distributions resulting in biased label imputation, which deteriorates the performance of SSL models. In this work, class transition tracking based Pseudo-Rectifying Guidance (PRG) is devised for MNAR. We explore the class-level guidance information obtained by the Markov random walk, which is modeled on a dynamically created graph built over the class tracking matrix. PRG unifies the historical information of class distribution and class transitions caused by the pseudo-rectifying procedure to maintain the model’s unbiased enthusiasm towards assigning pseudo-labels to all classes, so as the quality of pseudo-labels on both popular classes and rare classes in MNAR could be improved.”
- T. Shi, X. Ding, L. Zhang, X. Yang, FreeCOS: Self-Supervised Learning from Fractals and Unlabeled Images for Curvilinear Object Segmentation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
” This paper proposes a self-supervised curvilinear object segmentation method (FreeCOS) that learns robust and distinctive features from fractals and unlabeled images. The key contributions include a novel Fractal-FDA synthesis (FFS) module and a geometric information alignment (GIA) approach. FFS generates curvilinear structures based on the parametric Fractal L-system and integrates the generated structures into unlabeled images to obtain synthetic training images via Fourier Domain Adaptation.”
- L. Chen, C. Lei, R. Li, S. Li, Z. Zhang, L. Zhang, FPR: False Positive Rectification for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we present a False Positive Rectification (FPR) approach to tackle the co-occurrence problem by leveraging the false positives of CAM. Based on the observation that the CAM-activated regions of absent classes contain class-specific co-occurred background cues, we collect these false positives and utilize them to guide the training of CAM network by proposing a region-level contrast loss and a pixel-level rectification loss.”
Multimodal learning
- Y. Wang, Z. Cui, Y. Li, Distribution-Consistent Modal Recovering for Incomplete Multimodal Learning, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we propose a novel recovery paradigm, Distribution-Consistent Modal Recovering (DiCMoR), to transfer the distributions from available modalities to missing modalities, which thus maintains the distribution consistency of recovered data. In particular, we design a class-specific flow based modality recovery method to transform cross-modal distributions on the condition of sample class, which could well predict a distributionconsistent space for missing modality by virtue of the invertibility and exact density estimation of normalizing flow.”
Transformers
- P. K. Anasosalu Vasu, J. Gabriel, J. Zhu, O. Tuzel, A. Ranjan, FastViT: A Fast Hybrid Vision Transformer Using Structural Reparameterization, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“In this work, we introduce FastViT, a hybrid vision transformer architecture that obtains the state-of-the-art latency-accuracy trade-off. To this end, we introduce a novel token mixing operator, RepMixer, a building block of FastViT, that uses structural reparameterization to lower the memory access cost by removing skip-connections in the network.”
- Y. Chen, H. Liu, H. Yin, B. Fan, Building Vision Transformers with Hierarchy Aware Feature Aggregation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we propose the Hierarchy Aware Feature Aggregation framework (HAFA). HAFA enhances the extraction of local features adaptively in shallow layers where semantic information is weak, while is able to aggregate patches with similar semantics in deep layers. The clear semantic information of the aggregated patches, enables the attention mechanism to more accurately model global information at the semantic level.”
Domain generalization, transferability
- H. Xu, U. Kang, Fast and Accurate Transferability Measurement by Evaluating Intra-class Feature Variance, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“We view transferability as the generalization of a pre-trained model on a target task by measuring intra-class feature variance. Intra-class variance evaluates the adaptability of the model to a new task, which measures how transferable the model is. Compared to previous studies that estimate how discriminative the models are, intra-class variance is more accurate than those as it does not require an optimal feature extractor and classifier.”
- Z. Sun, Y. Sun, L. Yang, S. Lu, J. Mei, W. Zhao, Y. Hu, Unleashing the Power of Gradient Signal-to-Noise Ratio for Zero-Shot NAS, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“Neural Architecture Search (NAS) aims to automatically find optimal neural network architectures in an efficient way. In this paper, we not only explicitly give the probability that larger gradient signal-to-noise ratio (GSNR) at network initialization can ensure better generalization, but also theoretically prove that GSNR can ensure better convergence. Then we design the ξ-based gradient signal-to-noise ratio (ξ-GSNR) as a Zero-Shot NAS proxy to predict the network accuracy at initialization. “
- S. Hemati, G. Zhang, A. Estiri, X. Chen, Understanding Hessian Alignment for Domain Generalization, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we analyze the role of the classifier’s head Hessian matrix and gradient in domain generalization using recent OOD theory of transferability. Theoretically, we show that spectral norm between the classifier’s head Hessian matrices across domains is an upper bound of the transfer measure, a notion of distance between target and source domains. […] Finally, we propose two simple yet effective methods to match the classifier’s head Hessians and gradients in an efficient way, based on the Hessian Gradient Product (HGP) and Hutchinson’s method (Hutchinson), and without directly calculating Hessians.”
- M. Gholami, M. Akbari, X. Wang, B. Kamranian, Y. Zhang, ETran: Energy-Based Transferability Estimation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we propose ETran, an energy-based transferability assessment metric, which includes three scores: 1) energy score, 2) classification score, and 3) regression score. We use energy-based models to determine whether the target dataset is OOD or IND for the pre-trained model.”
Foundation models for medical imaging
- Z. Ji, D. Guo, P. Wang, K. Yan, L. Lu, M. Xu, Q. Wang, J. Ge, M. Gao, X. Ye, D. Jin, Continual Segment: Towards a Single, Unified and Non-forgetting Continual Segmentation Model of 143 Whole-body Organs in CT Scans, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
” we propose a new architectural continual semantic segmentation (CSS) learning framework to learn a single deep segmentation model for segmenting a total of 143 whole-body organs. Using the encoder/decoder network structure, we demonstrate that a continually trained then frozen encoder coupled with incrementally-added decoders can extract sufficiently representative image features for new classes to be subsequently and validly segmented, while avoiding the catastrophic forgetting in CSS.”
- V. Ion Butoi, J. J. Gonzalez Ortiz, T. Ma, M. R. Sabuncu, J. Guttag, A. V. Dalca, UniverSeg: Universal Medical Image Segmentation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“We present UniverSeg, a method for solving unseen medical segmentation tasks without additional training. Given a query image and an example set of image-label pairs that define a new segmentation task, UniverSeg employs a new CrossBlock mechanism to produce accurate segmentation maps without additional training.”
- J. Liu, Y. Zhang, J.-N. Chen, J. Xiao, Y. Lu, B. A. Landman, Y. Yuan, A. Yuille, Y. Tang, Z. Zhou, CLIP-Driven Universal Model for Organ Segmentation and Tumor Detection, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“we propose the CLIP-Driven Universal Model, which incorporates text embedding learned from Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) to segmentation models. This CLIPbased label encoding captures anatomical relationships, enabling the model to learn a structured feature embedding and segment 25 organs and 6 types of tumors.”
Efficient and scalable vision
- K. Wu, H. Peng, Z. Zhou, B. Xiao, M. Liu, L. Yuan, H. Xuan, M. Valenzuela, X. Chen, X. Wang, H. Chao, H. Hu, TinyCLIP: CLIP Distillation via Affinity Mimicking and Weight Inheritance, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“In this paper, we propose a novel cross-modal distillation method, called TinyCLIP, for large-scale language-image pre-trained models. The method introduces two core techniques: affinity mimicking and weight inheritance. Affinity mimicking explores the interaction between modalities during distillation, enabling student models to mimic teachers’ behavior of learning cross-modal feature alignment in a visual-linguistic affinity space. Weight inheritance transmits the pre-trained weights from the teacher models to their student counterparts to improve distillation efficiency.”
- P. Nooralinejad, A. Abbasi, S. A. Koohpayegani, K. P. Meibodi, R. M. Shahroz Khan, S. Kolouri, H. Pirsiavash, PRANC: Pseudo RAndom Networks for Compacting Deep Models, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“We demonstrate that a deep model can be reparametrized as a linear combination of several randomly initialized and frozen deep models in the weight space. During training, we seek local minima that reside within the subspace spanned by these random models (i.e., ‘basis’ networks). Our framework, PRANC, enables significant compaction of a deep model.”
Topology in deep learning models
- H. He, J. Wang, P. Wei, F. Xu, X. Ji, C. Liu, J. Chen, TopoSeg: Topology-Aware Nuclear Instance Segmentation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
” we develop a topology-aware segmentation approach, termed TopoSeg, which exploits topological structure information to keep the predictions rational, especially in common situations with densely touching and overlapping nucleus instances. Concretely, TopoSeg builds on a topology-aware module (TAM), which encodes dynamic changes of different topology structures within the three-class probability maps (inside, boundary, and background) of the nuclei to persistence barcodes and makes the topology-aware loss function.”
- M. J. Menten, J. C. Paetzold, V. A. Zimmer, S. Shit, I. Ezhov, R. Holland, M. Probst, J. A. Schnabel, D. Rueckert, A Skeletonization Algorithm for Gradient-Based Optimization, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
” This work introduces the first three-dimensional skeletonization algorithm that is both compatible with gradient-based optimization and preserves an object’s topology. Our method is exclusively based on matrix additions and multiplications, convolutional operations, basic non-linear functions, and sampling from a uniform probability distribution, allowing it to be easily implemented in any major deep learning library.”
Diverse
- Y. Wang, Y. Yue, R. Lu, T. Liu, Z. Zhong, S. Song, G. Huang, EfficientTrain: Exploring Generalized Curriculum Learning for Training Visual Backbones, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“This paper presents a new curriculum learning approach for the efficient training of visual backbones (e.g., vision Transformers). Our work is inspired by the inherent learning dynamics of deep networks: we experimentally show that at an earlier training stage, the model mainly learns to recognize some ‘easier-to-learn’ discriminative patterns within each example, e.g., the lower-frequency components of images and the original information before data augmentation.”
- P. Yang, C. G. M. Snoek, Y. M. Asano, Self-Ordering Point Clouds, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“In this paper we address the task of finding representative subsets of points in a 3D point cloud by means of a point-wise ordering. […] we introduce the task of point-wise ordering in 3D point clouds through self-supervision, which we call selfordering. We further contribute the first end-to-end trainable network that learns a point-wise ordering in a selfsupervised fashion. It utilizes a novel differentiable point scoring-sorting strategy and it constructs an hierarchical contrastive scheme to obtain self-supervision signals.”
- J. Yang, X. Ding, Z. Zheng, X. Xu, X. Li, GraphEcho: Graph-Driven Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Echocardiogram Video Segmentation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“In this paper, we introduce a newly collected CardiacUDA dataset and a novel GraphEcho method for cardiac structure segmentation. Our GraphEcho comprises two innovative modules, the Spatial-wise Cross-domain Graph Matching (SCGM) and the Temporal Cycle Consistency (TCC) module, which utilize prior knowledge of echocardiogram videos, i.e., consistent cardiac structure across patients and centers and the heartbeat cyclical consistency, respectively.”
- A. Schmidt, P. Morales-Álvarez, R. Molina, Probabilistic Modeling of Inter- and Intra-observer Variability in Medical Image Segmentation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“In this paper, we propose a novel model, called Probabilistic Inter-Observer and iNtraObserver variation NetwOrk (Pionono). It captures the labeling behavior of each rater with a multidimensional probability distribution and integrates this information with the feature maps of the image to produce probabilistic segmentation predictions. The model is optimized by variational inference and can be trained end-to-end.”
- M. Ladron de Guevara, J. Echevarria, Y. Li, Y. Hold-Geoffroy, C. Smith, D. Ito, Cross-modal Latent Space Alignment for Image to Avatar Translation, ICCV 2023. Link to the paper
“We present a novel method for automatic vectorized avatar generation from a single portrait image. […] we leverage modality-specific autoencoders trained on largescale unpaired portraits and parametric avatars, and then learn a mapping between both modalities via an alignment module trained on a significantly smaller amount of data.”